
When the invoice is paid, a second entry is made to debit accounts payable and credit the cash account– a reduction of cash. The balance sheet is a financial statement that shows a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a given point in time. Current liabilities are often separated out in a subcategory at the top of the liability section– the second section of the three. Yes, high current liabilities relative to current assets can negatively impact a company’s creditworthiness and financial stability. That is to say, notes and loans are usually listed first, then accounts payable, and finally accrued liabilities and taxes.
- If the working capital is low then it means the business has enough funds for settling the current liabilities but it doesn’t have enough for future investments.
- To account for non-current liabilities, a company must record them on their balance sheet, a financial statement listing a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity.
- The reported amount on the retailer’s balance sheet is the cost of merchandise that was purchased, but not yet sold to customers.
- Current assets include accounts receivable, inventory, marketable securities, prepaid expenses, and cash and cash equivalent.
- If a company’s board of directors declares dividends to be paid out to shareholders in the next twelve months, they will be recorded as current liabilities.
- A number higher than one is ideal for both the current and quick ratios, since it demonstrates that there are more current assets to pay current short-term debts.
Current Portions of Long-Term Debt

Also a stockholders’ equity account that usually reports the cost of the stock that has been repurchased. These provide additional information pertaining to a company’s operations and financial position and are considered to be an integral part of the financial statements. Liabilities also include amounts received in advance for a future sale or for a future service to be performed.
Cash Ratio
- On the other hand, insufficient working capital can indicate that a company does not have enough assets to meet its current liabilities, leading to short-term liquidity problems.
- Let’s examine how current liabilities can be distinguished from related terms.
- These items or financial events usually are not significant enough because they do not directly contribute to an organisation’s core operations.
- Current Lease Payable stands for the lease obligations due in the short-term, or in the next twelve months.
- The quick ratio determines whether a business has sufficient assets that it can turn to cash to pay back debts.
Some examples of contingent liabilities include pending litigation, product guarantees and warranties, and the guarantee of others’ indebtedness. Contract liabilities can be either current or non-current liabilities, depending on the timing of when the contract is expected to be fulfilled. normal balance Below are some of the highlights from the income statement for Apple Inc. (AAPL) for its fiscal year 2024.
Current Ratio Formula
- However, if the number is too high, it could mean the company is not leveraging its assets as well as it otherwise could be.
- Because current liabilities are payable in a relatively short period of time, they are recorded at their face value.
- While capital is not considered a liability, it does have an impact on a company’s financial health and ability to meet its obligations.
- The book value of a company is the amount of owner’s or stockholders’ equity.
- This indicates how much of a corporation’s assets are financed by lenders/creditors as opposed to purchased with owners’ or stockholders’ funds.
- At first, start-ups typically do not create enoughcash flow to sustain operations.
- Included in this category are accounts such as Accounts Payable, Trade Notes Payable, Current Maturities of Long-term Debt, Interest Payable, and Dividends Payable.
Since no interest is payable on December 31, 2023, this balance sheet will not report a liability for interest on this loan. Goodwill is an intangible asset that is recorded when a company buys another business for an amount that is greater than the fair value of the identifiable assets. To illustrate, assume that a corporation pays $5 million to acquire a business that has tangible and identifiable intangible assets having a fair value of $4 million. The long-term asset construction in progress accumulates a company’s costs of constructing new buildings, additions, equipment, etc.
Also, if the company had an obligation to pay employees a pension or other post-retirement benefits such as health care, those items would be mostly long-term liabilities. Warranty liabilities are estimated costs to repair or replace products under warranty. This liability reflects a company’s commitment to quality what are liabilities in accounting and customer service. For instance, a manufacturer estimates $10,000 for potential warranty claims on products sold within the year. A firm may receive cash in advance of performing some service or providing some goods.
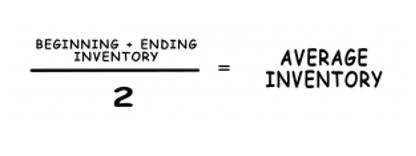
Inventory
Summarising the core difference between current liabilities and other current liabilities, the former is significant to a company’s core operations and therefore precisely recorded in its books. At the same time, the latter is less significant and ergo lumped together under a single heading. Interest payable is a liability towards interest expenses that has been incurred but yet to be paid as on the date of balance sheet. A distribution of part of a corporation’s past profits to its stockholders. (Some corporations have preferred stock in addition to their common stock.) Shares of common stock provide evidence of ownership in a corporation. Holders of common stock elect the corporation’s directors and share in the distribution of profits of the company via dividends.
Short-term loans payable

The actual amount of such liabilities cannot be determined until the said event occurs, which means that these liabilities must be estimated for accounting purposes. What’s more, many times, the actual payee of the liability is not known either until the future event occurs. All current liabilities that are known and have a definite Partnership Accounting amount fall under this category. Some examples of definitely determinable current liabilities include Accounts Payable, Trade Notes Payable, Current Maturities of Long-Term Debt, Dividends Payable, and Interest Payable.
An educational institution, for instance, receives $50,000 in tuition fees for the upcoming semester, to be recognized as revenue over the course of the semester. Customer deposits are payments received from customers for products or services to be delivered in the future. These deposits represent a company’s obligation to fulfill its commitments. For example, a hotel collects $5,000 in deposits for future room bookings, which will be recognized as revenue when the service is provided.

